The CryptoWall ransomware virus is getting a lot of attention lately but this is one angle I haven’t seen covered: how to get an alert in the MaxFocus (formerly GFI) dashboard if a machine is infected. The sooner you know, the sooner you can work on restoring a current backup.
Here’s a standalone PowerShell script that checks a few file and registry locations for evidence of CryptoWall and raises an error if found.
This approach has been called “canary in the coalmine” virus notification: if it trips, the machine is infected. Note that it does nothing about preventing an infection; it is purely an after-the-fact alert.
Test and use this at your own risk. If you find a bug, or have a suggestion for a file or registry path that is not checked, leave a comment.
Compatibility and Functionality
The script should work on XP/2003 and above, and PowerShell 2 and above. It only works on U.S. English (and possibly other English) locales due to some hard-coded file paths (“Documents” etc.).
The script checks for DECRYPT_INST*.* files in two public folders and in three folders in each user’s profile. It also checks the registry for known CryptoLocker Decrypter keys. See more details in the script code and comments.
Update 11 December 2015 The script has been enhanced to also check for the patterns HELP_DECRYPT*.* and HELP_YOUR_FILES*.* so it can detect CryptoWall 3.0 and 4.0 infections respectively. See details in this post.
Update 19 April 2016 Additional patterns have been added and may be added in the future. See the changelog in the script for details.
Primary references used:
http://www.pcsgo.com/quickly-remove-cryptowall-decrypter-from-your-computer-ransomware-removal-guides/
http://www.virusresearch.org/remove-cryptowall-manually/
http://www.bleepingcomputer.com/virus-removal/cryptowall-ransomware-information
Use in MaxFocus
If you deploy the script to MaxFocus, you should see a quick summary of the results in the dashboard:
Hopefully you won’t see this:
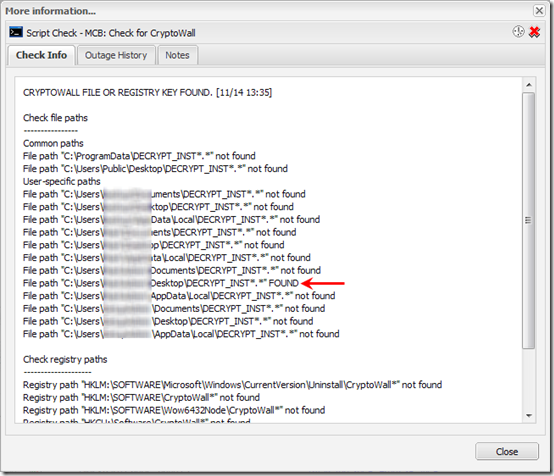
If you click on the blue text, a window appears with more detail:
The script runs very fast, a few seconds at most. Set it up in MaxFocus as a 24×7 check with Outage notification by email and/or SMS. Depending on how often your checks run, you should know of an infection within an hour at most.
The Script
Copy and paste this as a PowerShell script (e.g. CheckCryptoWall.ps1).
<#
.Synopsis
Check for the existence of some common CryptoWall files and registry keys.
This is not a comprehensive threat detection engine, and it does NOTHING to
prevent or block the threat. It just checks for the presence of decryption
instructions in some common folders, and for the presence of some registry
keys used by the CryptoWall Decrypter. Hopefully if you find out right away
that you have an encrypted machine, you can restore it from a recent backup.
Only handles U.S. (and maybe other English) locales.
Copyright (c) 2016 by MCB Systems. All rights reserved.
Free for personal or commercial use. May not be sold.
No warranties. Use at your own risk.
Can be used with MaxFocus Advanced Monitoring Agent.
Returns summary line first, followed by list of paths checked. The
summary will be visible in the MaxFocus dashboard as a hyperlink.
When you click on the hyperlink, the details display in a window.
Returns exit code 1001 if matching path found. This will cause the
MaxFocus check to fail and optionally to send an alert.
References:
http://www.pcsgo.com/quickly-remove-cryptowall-decrypter-from-your-computer-ransomware-removal-guides/
http://www.virusresearch.org/remove-cryptowall-manually/
http://www.bleepingcomputer.com/virus-removal/cryptowall-ransomware-information
.Notes
Name: MCB.CheckCryptoWall.ps1
Author: Mark Berry, MCB Systems
Created: 11/14/2014
Last Edit: 05/21/2016
Changes:
12/11/2015 Allow $FilePatterns parameter to be a comma-separated list of patterns.
Add HELP_DECRYPT*.* and HELP_YOUR_FILES*.* to the list, to detect
CryptoWall 3.0 and 4.0 infections respectively. See
http://www.bleepingcomputer.com/virus-removal/cryptowall-ransomware-information.
03/09/2016 Add *RECOVER_INSTRUCTIONS.* to $FilePatterns to include Locky cryptoware per
https://www.pcrisk.com/removal-guides/9807-locky-ransomware.
04/19/2016 Add *.FUN, *.KKK, *.GWS, and *.BTC to detect Jigsaw ransomware per
http://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/jigsaw-ransomware-decrypted-will-delete-your-files-until-you-pay-the-ransom/.
05/21/2016 Add DE_CRYPT*.* to detect CryptXXX. Note that CryptXXX 2.0 uses unique file names
for ransom messages and cannot be detected with this script.
https://www.proofpoint.com/threat-insight/post/cryptxxx2-ransomware-authors-strike-back-against-free-decryption-tool
.Parameter FilePatterns
Comma-separated list of filenames to look for in the hard-coded list of paths.
Wildcards allowed. Do not include backslash.
Default: Updated frequently. See parameter below.
.Parameter LogFile
Path to a log file. Required by GFI MAX script player. Not used here.
Default: "".
#>
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false,
Position = 0,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName = $true)]
[String]$FilePatterns="DECRYPT_INST*.*,HELP_DECRYPT*.*,HELP_YOUR_FILES*.*,*RECOVER_INSTRUCTIONS.*,*.FUN,*.KKK,*.GWS,*.BTC,DE_CRYPT*.*",
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false,
Position = 1,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName = $true)]
[String]$LogFile=""
)
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Define functions
# ----------------------------------------------------------
function CheckFilePath( `
[String]$FilePath="", `
[String[]]$FilePatternArray="", `
[ref]$OutputDetail) {
$CheckFilePath = $false # Default to false; exceptions below
# Loop through each $FilePattern in the $FilePatternArray
ForEach ($FilePattern in $FilePatternArray) {
$FileFullPath = $FilePath + "\" + $FilePattern
if (Test-Path $FileFullPath) {
$OutputDetail.value += ("`n--->File path """ + $FileFullPath + """ FOUND <---")
$CheckFilePath = $true
} else {
$OutputDetail.value += ("`nFile path """ + $FileFullPath + """ not found")
}
}
return $CheckFilePath
}
function CheckRegistryPath( `
[String]$RegistryPath="", `
[ref]$OutputDetail) {
if (Test-Path $RegistryPath) {
$OutputDetail.value += ("`n--->Registry path """ + $RegistryPath + """ FOUND <---")
$CheckRegistryPath = $true
} else {
$OutputDetail.value += ("`nRegistry path """ + $RegistryPath + """ not found")
$CheckRegistryPath = $false
}
return $CheckRegistryPath
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Initialize variables
# ----------------------------------------------------------
$CryptoWallFound = $false
$OutputDetail = "" # Will build up a string in this variable to be output AFTER summary line
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Check file paths
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Parse $FilePatterns parameter into an array by splitting on commas
$FilePatternArray = $FilePatterns.split(",")
# Per http://www.bleepingcomputer.com/virus-removal/cryptowall-ransomware-information, CryptoWall
# puts DECRYPT_INSTRUCTION.TXT, .URL, and .HTML files in every encrypted folder. Check a few common folders.
# 12/11/2015: CryptoWall 3.0 and 4.0 place HELP_DECRYPT*.* and HELP_YOUR_FILES*.*, respectively.
$OutputDetail += "`nCheck file paths"
$OutputDetail += "`n----------------"
$OutputDetail += "`nCommon paths"
$SpecialFolder = [environment]::getfolderpath("CommonApplicationData")
if (CheckFilePath($SpecialFolder) $FilePatternArray ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
# Because we run this as the SYSTEM user under MaxFocus, we need to "manually" derive
# the paths to users' folders (on XP or Vista/7/8), then loop through them.
$ProfileRoot = $env:SystemDrive + "\Users"
if (Test-Path $ProfileRoot) { # Windows Vista/7/8/10/2008/2008R2/2012/2012R2
# [environment]::getfolderpath("CommonDesktopDirectory") not available in PowerShell 2 so code path directly
if (CheckFilePath($ProfileRoot + "\Public\Desktop") $FilePatternArray ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
$OutputDetail += "`nUser-specific paths"
# List directories ("containers") only in the $ProfileRoot path. Exclude hidden folders and junction points.
get-childitem $ProfileRoot | Where-Object { $_.PSIsContainer } | ForEach-Object {
# $_.Name is directory name only; $_.FullName includes full path
if ($_.Name -ne "Public") { # We handle common (Public) paths above
if (CheckFilePath($_.FullName + "\Documents") $FilePatternArray ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
if (CheckFilePath($_.FullName + "\Desktop") $FilePatternArray ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
if (CheckFilePath($_.FullName + "\AppData\Local") $FilePatternArray ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
}
}
} else { # should be XP/2003
$ProfileRoot = $env:SystemDrive + "\Documents and Settings"
if (Test-Path $ProfileRoot) {
# [environment]::getfolderpath("CommonDesktopDirectory") not available in PowerShell 2 so code path directly
if (CheckFilePath($ProfileRoot + "\All Users\Desktop") $FilePatternArray ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
$OutputDetail += "`nUser-specific paths"
# List directories ("containers") only in the $ProfileRoot path. Exclude hidden folders and junction points.
get-childitem $ProfileRoot | Where-Object { $_.PSIsContainer } | ForEach-Object {
# $_.Name is directory name only; $_.FullName includes full path
if ($_.Name -ne "All Users") { # We handle common (All Users) paths above
if (CheckFilePath($_.FullName + "\My Documents") $FilePatternArray ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
if (CheckFilePath($_.FullName + "\Desktop") $FilePatternArray ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
if (CheckFilePath($_.FullName + "\Local Settings\Application Data") $FilePatternArray ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
}
}
}
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Check registry paths
# ----------------------------------------------------------
$OutputDetail += "`n`nCheck registry paths"
$OutputDetail += "`n--------------------"
# From http://www.pcsgo.com/quickly-remove-cryptowall-decrypter-from-your-computer-ransomware-removal-guides/
# This only checks the existence of registry _keys_, not values
# Most keys are "CryptoWall Decrypter" but use a wildcard "CryptoWall*" for a slightly more generic search.
if (CheckRegistryPath "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\CryptoWall*" ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
if (CheckRegistryPath "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\CryptoWall*" ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
# I'm also adding searches under Wow6432Node in case it gets deployed as a 32-bat app on a 64-bit platform:
if (CheckRegistryPath "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\CryptoWall*" ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
if (CheckRegistryPath "HKCU:\Software\CryptoWall*" ([ref]$OutputDetail)) { $CryptoWallFound = $true }
# Note: Not all keys in those articles are added here. Some keys look like legitimate Windows settings
# that CryptoWall manipulates, e.g. turning off System Restore. Some keys require checking values,
# which PowerShell's Test-Path does not do.
if ($CryptoWallFound) {
$Status = "CRYPTOWALL FILE OR REGISTRY KEY FOUND."
$ExitCode = 1001
}
else {
$Status = "No CryptoWall files or registry keys found."
$ExitCode = 0
}
#Print SummaryLine for display in monitoring system. Abbreviate date/time.
$Status + " [" + (Get-Date -Format "MM/dd HH:mm") + "]"
$OutputDetail
"`n======================================================"
"`nLocal Machine Time: " + (Get-Date -Format G)
"Exit Code: " + $ExitCode
Exit $ExitCode